Pain or Inflammation treatment
6am - midnight, 7 days a week
Accessible from anywhere in Australia.
eScript in minutes
Medication delivery
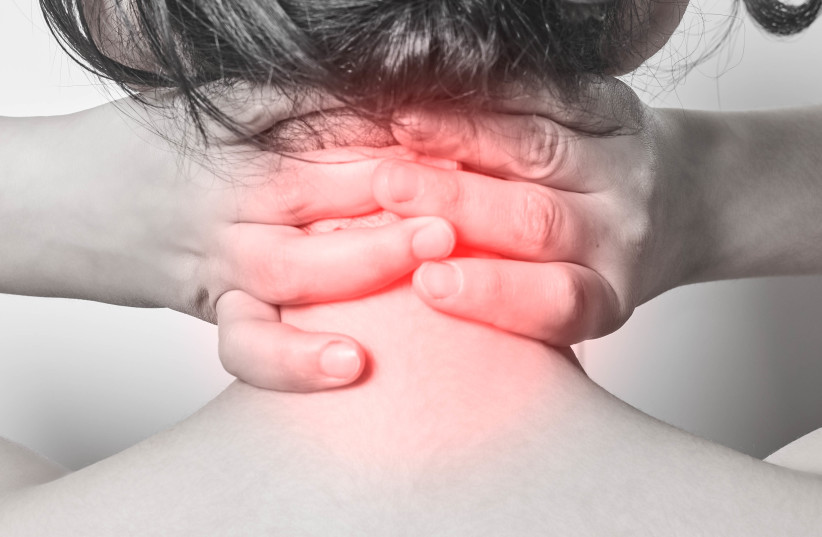
What is chronic pain?
Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists beyond the usual healing period following an injury or illness, typically lasting for 3 to 6 months or longer. This type of pain can vary in intensity from mild to severe and is experienced on most days of the week.
Pain or Inflammation Treatment Options

Online Prescriptions
- For when your script has run out
- Script sent to your phone
- Doctor approved

Telehealth Consultations
- When you need to speak to a doctor
- Online, Video & Phone Call or Message
- Fast access to medical advice
Medical Certificates
- For when your script has run out
- Script sent to your phone
- Doctor approved

Pain or Inflammation Symptoms
Pain and inflammation are common responses to injury, infection, or chronic conditions, often signaling the body’s healing process. Symptoms of pain may range from mild discomfort to severe, sharp, or throbbing sensations, while inflammation typically presents with redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area. These symptoms can be acute and short-term or chronic, persisting for weeks or even years, depending on the underlying cause.
Dangers of Pain or Inflammation
While occasional pain and inflammation are part of the body’s natural defense mechanisms, prolonged or unmanaged symptoms can lead to serious complications. Chronic inflammation is linked to conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Persistent pain can impair mobility, disrupt sleep, and negatively affect mental health, contributing to anxiety, depression, or reduced quality of life. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle modifications are essential to managing symptoms effectively and preventing long-term health risks.

Need a Specialist Referral?Get Yours in a Few Simple Steps!
Skip the long clinic waits and get referred to a specialist in minutes. The process is fast, secure, and simple.
- Quick access to specialist referrals – no in-person appointments needed
- Telehealth consultations with trusted, licensed doctors
- Fast, reliable service – referrals sent directly to your chosen specialist
- Convenient and affordable healthcare from your home
- No hidden costs – just simple, upfront pricing
Frequently
Asked Questions
Pain and inflammation occur as part of the body’s natural defense and healing processes. They can result from injuries, infections, autoimmune disorders, or chronic conditions like arthritis. Inflammation is the immune system’s way of protecting damaged tissues and fighting harmful invaders, but it can sometimes become persistent or excessive, leading to discomfort or long-term issues.
Acute pain is a temporary response to injury or illness and typically resolves as the underlying issue heals. Chronic pain, on the other hand, lasts for months or even years, often continuing after the initial cause has been treated. Chronic pain is frequently associated with long-term inflammation or conditions like nerve damage and arthritis.
Inflammation is the body’s natural reaction to injury or infection, designed to promote healing. When the immune system detects a problem, it sends signals that increase blood flow to the affected area, causing redness, swelling, and sometimes pain. While this response is helpful in the short term, chronic inflammation can occur when the immune system stays active unnecessarily, potentially leading to tissue damage.
Inflammation is often characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain in the affected area. It can also cause stiffness or reduced function, depending on the location and severity. In some cases, such as with internal inflammation, symptoms may be less obvious, leading to fatigue or general discomfort without visible signs.
Yes, not all inflammation is accompanied by pain. In chronic conditions, low levels of inflammation can persist silently, causing gradual damage to tissues over time. This type of “silent inflammation” is often linked to diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, or certain autoimmune disorders.
Inflammation can irritate surrounding nerves, triggering pain signals. This connection is particularly evident in conditions like arthritis or tendinitis, where swelling directly impacts nerve endings. The pain serves as a warning sign, prompting rest or medical attention to avoid further damage.
Lifestyle factors such as an unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, stress, and smoking can contribute to ongoing inflammation. Obesity is another common factor, as excess fat tissue can release inflammatory chemicals into the bloodstream. Addressing these triggers can help manage or prevent chronic inflammation.

