Cholesterol treatment
6am - midnight, 7 days a week
Accessible from anywhere in Australia.
eScript in minutes
Medication delivery
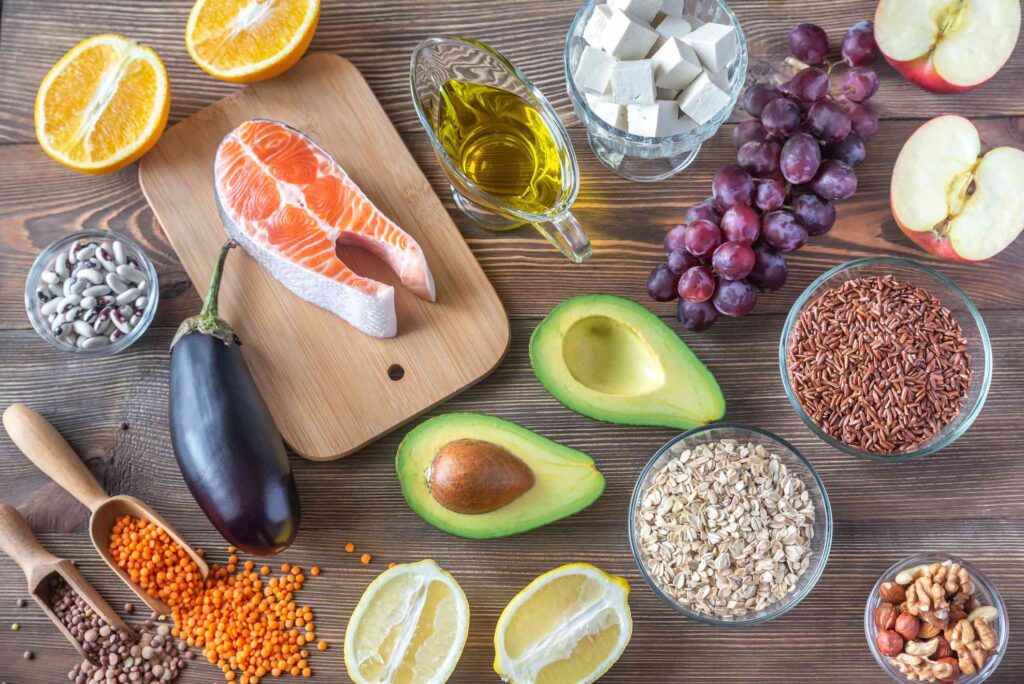

What is high cholesterol?
High cholesterol occurs when there is an excessive amount of cholesterol in the blood, which can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries. This increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Cholesterol is categorised into low density lipoprotein (LDL), often called “bad” cholesterol, and high density lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good” cholesterol.
Cholesterol Treatment Options

Online Prescriptions
- For when your script has run out
- Script sent to your phone
- Doctor approved

Telehealth Consultations
- When you need to speak to a doctor
- Online, Video & Phone Call or Message
- Fast access to medical advice
Medical Certificates
- For when your script has run out
- Script sent to your phone
- Doctor approved
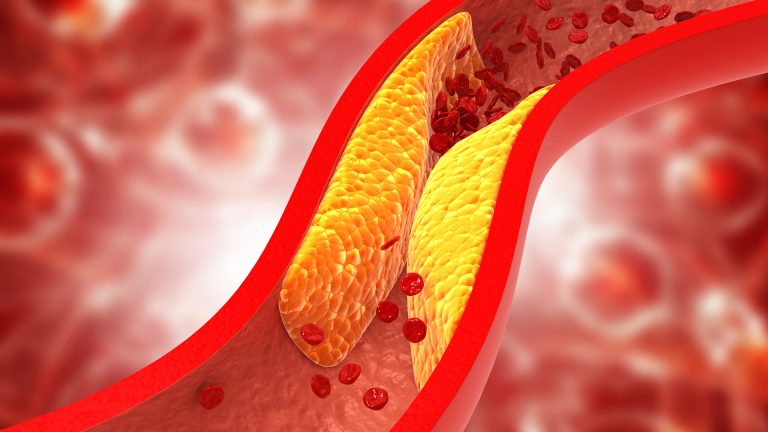
Cholesterol Symptoms
High cholesterol typically does not cause noticeable symptoms, which is why it is often referred to as a “silent” condition. It is usually detected through routine blood tests. However, in advanced cases, complications may arise, including:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Numbness or tingling in extremities due to poor circulation
Causes / Dangers / Complications of High Cholesterol
- Causes: High cholesterol can be caused by genetics, unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, obesity, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes.
- Dangers: Excess cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Complications: Uncontrolled high cholesterol can result in atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), heart disease, stroke, and reduced blood circulation to vital organs.
Regular cholesterol screenings and lifestyle modifications can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of serious health complications.
Need a Specialist Referral?Get Yours in a Few Simple Steps!
Skip the long clinic waits and get referred to a specialist in minutes. The process is fast, secure, and simple.
- Quick access to specialist referrals – no in-person appointments needed
- Telehealth consultations with trusted, licensed doctors
- Fast, reliable service – referrals sent directly to your chosen specialist
- Convenient and affordable healthcare from your home
- No hidden costs – just simple, upfront pricing
Frequently
Asked Questions
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in two main forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can build up in the walls of your arteries, leading to blockages. HDL, known as “good” cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
High cholesterol can result from a combination of factors, including an unhealthy diet high in saturated and trans fats, lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and genetics. Some medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypothyroidism, can also contribute to elevated cholesterol levels.
Cholesterol levels are measured with a blood test called a lipid panel. This test provides information about your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Your doctor will interpret these results to determine whether your levels are within a healthy range or if treatment is needed.
High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Excess LDL cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaques in your arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which narrows and stiffens the arteries, impeding blood flow. Over time, this increases the likelihood of serious complications.
Treatment for high cholesterol often involves lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. In some cases, medications like statins, bile acid sequestrants, or cholesterol absorption inhibitors may be prescribed to lower LDL levels and improve overall cholesterol balance.
Preventing high cholesterol often involves lifestyle modifications. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while avoiding saturated fats and trans fats is crucial. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use also play essential roles in keeping cholesterol levels within a healthy range.
A healthy cholesterol level depends on several factors, including age, gender, and overall health. Generally, total cholesterol should be less than 200 mg/dL, LDL cholesterol less than 100 mg/dL, and HDL cholesterol above 40 mg/dL for men and 50 mg/dL for women. Triglycerides should remain below 150 mg/dL.

